How to operate a drone: Mastering the art of piloting an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of drone operation, covering pre-flight checks, control mechanisms, camera techniques, and essential maintenance procedures. We’ll explore everything from navigating airspace regulations to troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re equipped to fly confidently and responsibly.
This detailed exploration delves into the intricacies of drone flight, addressing both the theoretical and practical aspects. We will navigate the complexities of drone technology, from understanding the various control schemes and flight modes to mastering the art of capturing stunning aerial imagery. Furthermore, we will emphasize the importance of safety and legal compliance throughout the process, ensuring responsible and enjoyable drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, verifying battery levels, and confirming compliance with local regulations. Failing to perform these checks can lead to accidents or legal issues.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone is in optimal condition. This involves visually inspecting all components for any damage or wear and tear.
| Checklist Item | Importance | Potential Consequences of Failure | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propeller Inspection | Ensures proper balance and prevents crashes. | Unbalanced propellers can cause vibrations, instability, and potential crashes. | Visually inspect for cracks, chips, or bending. Replace damaged propellers. |
| Battery Level Check | Sufficient power is vital for a successful flight. | Low battery can cause sudden power loss and uncontrolled descent. | Check battery indicator and ensure sufficient charge for the planned flight duration. |
| Gimbal and Camera Function Test | Ensures proper camera operation. | Malfunctioning gimbal or camera can result in unusable footage. | Test camera movement and image quality. |
| GPS Signal Acquisition | Essential for stable flight and accurate positioning. | Loss of GPS signal can lead to uncontrolled flight and potential crashes. | Ensure sufficient satellite signals are acquired before takeoff. |
Airspace Regulations and Legal Requirements
Operating a drone legally requires understanding and adhering to various regulations. These regulations vary depending on location and drone type. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines or legal repercussions.
- Register your drone with the relevant aviation authority.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and property.
- Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Adhere to speed and altitude limitations.
- Fly only during daylight hours or in conditions with good visibility.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to react in case of emergencies is crucial. Quick and appropriate actions can mitigate potential damage or injury.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately engage Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually control the drone back to a safe location. If this is not possible, prepare for a controlled crash in a safe, open area.
- Battery Failure: Initiate RTH immediately if possible. If not, attempt a controlled descent to the nearest safe landing area. Be prepared for a potential crash landing.
- Motor Malfunction: Attempt to land safely in a clear area. If the drone becomes uncontrollable, prepare for a potential crash landing, prioritizing safety over equipment.
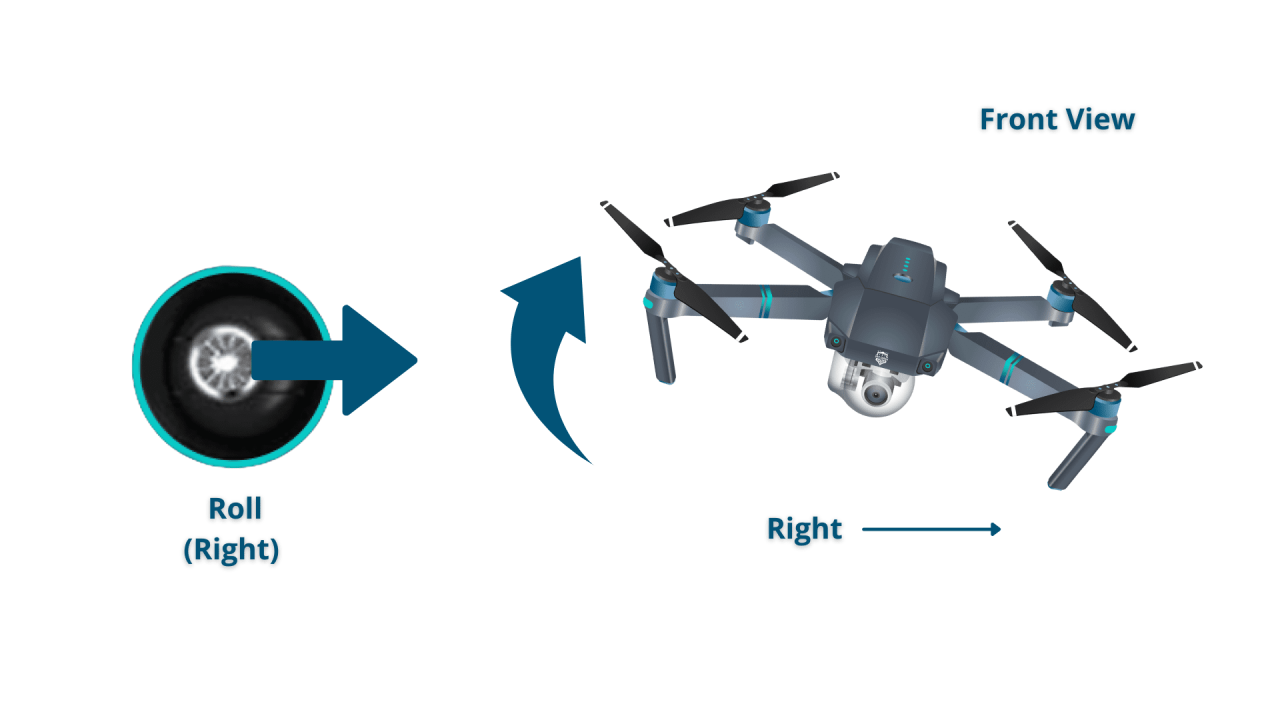
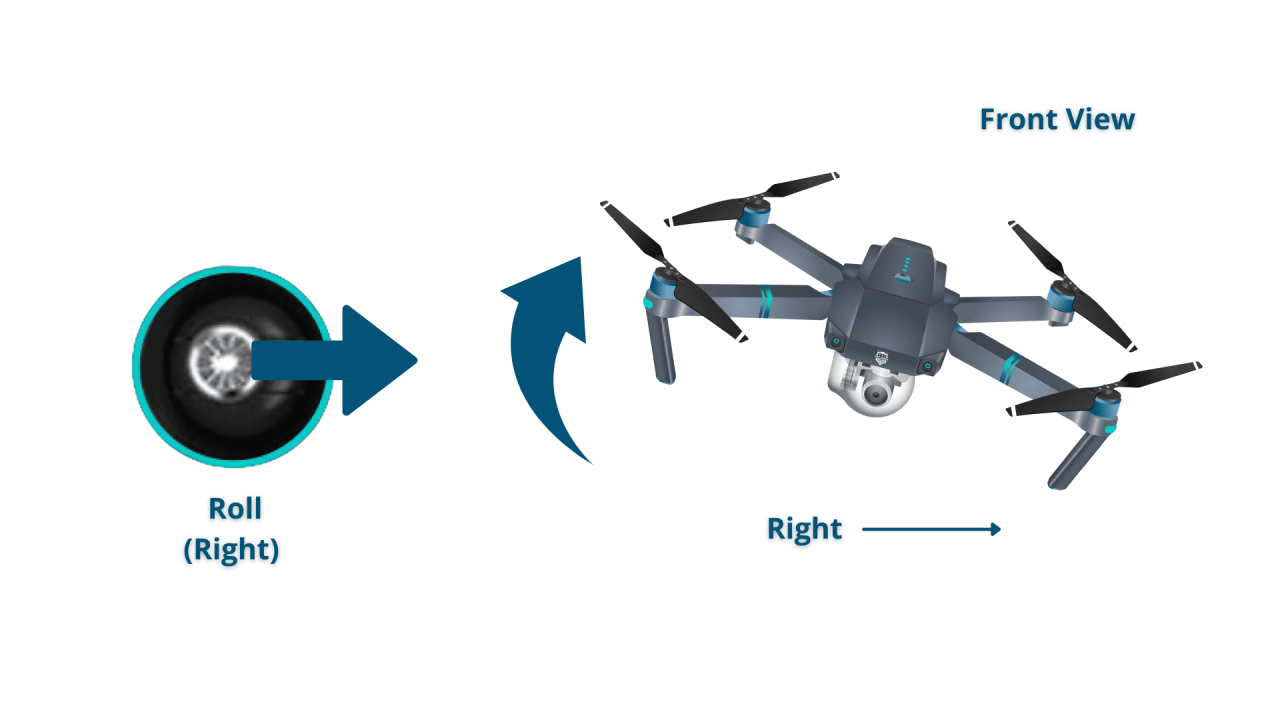
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones may use varying control schemes, and each flight mode offers distinct capabilities.
Drone Control Schemes
Most drones utilize sticks or joysticks for controlling movement. Understanding their functions is crucial for smooth operation.
| Control Type | Function of Stick/Joystick 1 | Function of Stick/Joystick 2 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard RC Controller | Yaw (rotation) and Throttle (altitude) | Pitch (forward/backward) and Roll (left/right) | This is a common configuration, but variations exist. |
| Smartphone App Control | On-screen virtual joysticks mimic the functionality of physical sticks. | N/A (typically combined) | Offers intuitive control for beginners, but may lack precision. |
Flight Modes

Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Choosing the appropriate mode is crucial for safe and stable operation.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning basic maneuvers.
- Sport Mode: Enables higher speeds and increased responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for stable hovering and precise positioning, beneficial for aerial photography.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains drone orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of GPS signal.
Beginner Drone Control Tutorial
This tutorial guides beginners through basic maneuvers. Practice in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people.
- Takeoff: Gently push the throttle stick upwards. The drone should ascend smoothly.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle position to keep the drone at a constant altitude.
- Movement: Use the pitch and roll sticks to move the drone forward, backward, left, and right. Small, controlled movements are key.
- Landing: Gently lower the throttle stick to bring the drone down slowly and smoothly.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography Techniques
The drone’s camera offers versatile capabilities for capturing stunning aerial footage. Understanding camera settings and photography techniques enhances image quality.
Camera Settings and Their Impact
Adjusting camera settings is essential for optimizing image quality in various conditions. Each setting plays a crucial role in the final output.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera. A wider aperture (lower f-number) results in a shallower depth of field, blurring the background. A narrower aperture (higher f-number) increases depth of field, keeping both foreground and background in focus.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds create motion blur.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values produce cleaner images with less noise, while higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions but introduce more noise.
Aerial Photography and Videography Techniques
Achieving high-quality aerial footage requires attention to composition, lighting, and stabilization.
- Composition: Utilize the rule of thirds to create visually appealing images. Consider leading lines and symmetry.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm light. Avoid harsh midday sun.
- Stabilization: Use a gimbal for smooth, stable footage, especially when flying in windy conditions.
Optimizing Camera Settings for Various Scenarios
Adjusting camera settings optimizes footage in diverse conditions. Understanding these adjustments is crucial for consistent quality.
- Low-Light Conditions: Increase ISO (but be mindful of noise), use a wider aperture, and slow down shutter speed (but avoid motion blur if the subject is moving).
- Fast-Moving Subjects: Increase shutter speed to freeze motion, potentially sacrificing some light.
Battery Management and Flight Time Optimization
Proper battery care and management are vital for extending battery lifespan and maximizing flight time. Understanding factors affecting battery consumption is key.
Battery Care and Maintenance
Following best practices extends battery life and ensures optimal performance.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid fully discharging or overcharging batteries.
- Use a proper battery charger.
- Inspect batteries regularly for damage.
Factors Affecting Battery Consumption
Various factors influence battery drain. Understanding these allows for better flight planning.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures (hot or cold) reduce battery performance.
- Wind: Flying against strong winds increases battery consumption.
- Flight Maneuvers: Aggressive maneuvers (rapid ascents, descents, and turns) consume more power.
Maximizing Flight Time
Strategic planning and battery management extend flight time while ensuring safety.
- Plan efficient flight paths to minimize unnecessary maneuvers.
- Monitor battery levels closely during flight.
- Land with sufficient battery reserve to avoid unexpected power loss.
Post-Flight Procedures and Data Management
Safe post-flight procedures and efficient data management are essential for preserving the drone and its captured footage. These steps ensure the longevity of the equipment and the accessibility of the data.
Safe Landing and Storage
Proper landing and storage protect the drone from damage.
- Land the drone gently in a clear, level area.
- Power off the drone.
- Remove the propellers (if necessary).
- Store the drone in a safe, dry place away from extreme temperatures.
- Store batteries separately, in a safe and appropriate manner.
Downloading and Managing Drone Footage
Efficiently downloading and managing footage ensures easy access and organization.
- Connect the drone to your computer or mobile device.
- Use the drone’s software to download the footage.
- Create a well-organized file structure to store the footage.
Organizing and Archiving Drone Footage, How to operate a drone
Well-organized footage is easily retrievable and convenient for editing.
- Use descriptive file names (e.g., date, location, subject).
- Create backups of your footage to prevent data loss.
- Consider using cloud storage for additional security.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their causes allows for quick resolution. Knowing how to troubleshoot these issues minimizes downtime and ensures smooth operation.
Common Drone Problems and Their Causes
| Problem | Potential Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, interference, weak signal | Check GPS indicator, move to an open area | Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky |
| Motor Malfunction | Motor damage, loose connections | Inspect motors, check connections | Replace damaged motors, tighten connections |
| Battery Issues | Low battery, faulty battery | Check battery level, inspect battery | Charge battery, replace faulty battery |
| Gimbal Malfunction | Mechanical failure, software glitch | Check gimbal movement, restart drone | Repair or replace gimbal, update firmware |
Troubleshooting Steps
A systematic approach to troubleshooting ensures efficient problem resolution.
- Identify the problem.
- Check for obvious causes (e.g., low battery, loose connections).
- Consult the drone’s manual for troubleshooting guidance.
- Contact the manufacturer’s support if the problem persists.
Drone Maintenance and Upkeep: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance extends the drone’s lifespan and ensures optimal performance. A scheduled maintenance plan prevents unexpected issues and ensures safety.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency | Tools/Materials | Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Before each flight | None | Check for damage to propellers, body, and other components. |
| Cleaning | After each flight | Soft cloth, mild detergent | Wipe down the drone body, propellers, and camera lens gently. |
| Battery Care | Regularly | Battery charger | Charge and store batteries properly. Avoid overcharging or discharging. |
| Firmware Update | As needed | Computer, drone software | Update the drone’s firmware to fix bugs and improve performance. |
Tools and Materials for Drone Maintenance
- Soft cloth
- Mild detergent
- Isopropyl alcohol (for cleaning)
- Propeller wrench (if applicable)
- Screwdrivers (if applicable)
Cleaning and Inspecting Drone Components
Detailed cleaning and inspection of the drone’s components are essential for optimal performance and safety.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully piloting a drone requires understanding its capabilities and limitations, and for a comprehensive guide, you should check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone This will help you confidently navigate the skies and capture stunning aerial footage. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount, so proper training is essential.
- Propeller Cleaning: Gently wipe each propeller with a soft cloth to remove dirt and debris. Inspect for cracks or damage; replace if necessary. A detailed image would show a close-up of a propeller, highlighting any chips, cracks, or bends.
- Body Cleaning: Use a soft cloth and mild detergent solution to wipe down the drone’s body. Avoid using harsh chemicals. A detailed image would show the careful wiping of the drone body with a soft cloth, emphasizing the gentle motion.
- Camera Lens Cleaning: Use a microfiber cloth or lens cleaning pen to gently clean the camera lens. Avoid touching the lens surface directly. A detailed image would show the correct way to clean a camera lens, using a microfiber cloth in a circular motion, starting from the center and moving outwards.
- Motor Inspection: Carefully inspect each motor for any damage or loose connections. Listen for unusual sounds during operation. A detailed image would showcase a close-up of each motor, highlighting the condition of the wires and any signs of wear and tear.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical skill, responsible decision-making, and a commitment to safety. By understanding pre-flight checks, mastering the controls, and adhering to legal regulations, you can unlock the potential of this exciting technology. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to refining your skills and ensuring safe and enjoyable flights. Soar responsibly and capture breathtaking moments from above!
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Beginner-friendly drones typically feature GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functions, and user-friendly interfaces. Look for models with good reviews and ample online tutorials.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide will help you understand everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you’re comfortable and confident operating your drone responsibly.
How do I obtain a drone pilot license or permit?
Licensing requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures. Many countries require registration of the drone itself, even without a pilot license.
What is the maximum flight time for most drones?
Flight time depends heavily on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, temperature). Expect flight times ranging from 15-30 minutes for many consumer drones, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Most modern drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately if you lose control. If the RTH fails, attempt to regain control using the emergency procedures Artikeld in your drone’s manual. If it still doesn’t respond, contact local authorities.